Risk factors for Renal and Gall Bladder Stone

Risk factors for Renal (kidney) Stone
Kidney stones
Anyone can get a kidney stone, but some people are more likely than others to have them. Men get kidney stones more often than women do. Kidney stones are also more common in non-Hispanic white people than in people of other ethnicities. You may also be more likely to have kidney stones if:
• You have had kidney stones before.
• Someone in your family has had kidney stones.
• You don't drink enough water.
• You follow a diet high in protein, sodium and/or sugar.
• You are overweight or obese.
• You have had gastric bypass surgery or another intestinal surgery.
• You have polycystic kidney disease or another cystic kidney disease.
• You have a certain condition that causes your urine to contain high levels of cystine, oxalate, uric acid or calcium.
• You have a condition that causes swelling or irritation in your bowel or your joints.
• You take certain medicines, such as diuretics (water pills) or calcium-based antacids.
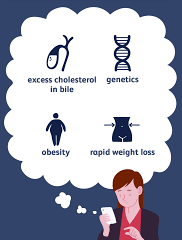
Risk factors for Gall Bladder Stone
While your body produces cholesterol naturally, you can also take in excess cholesterol through your diet. Many risk factors for gallstones are related to diet.
These include:
• Being overweight or obese
• Eating a diet that's high in fat or cholesterol
• Rapid weight loss within a short period of time
• Eating diet that's high in fiber
• Having diabetes mellitus
• Being female
• Being of American Indian or cholesterol
• Rapid weight loss within a short period of time
• Eating diet that's high in fiber
• Having diabetes mellitus
• Being female
• Being of American Indian or Mexican-American descent
• Being pregnant
• Having a family history of gallstones
• Being age 60 or older
• Having cirrhosis of the liver
• Taking certain medications for lowering cholesterol
• Taking medications that have a high estrogen content